What is The Meaning of Semantics in Linguistics?
The term “semantics” refers to the study of how information is effectively conveyed from one person to another. The word “semantics” is derived from the Greek word σημαντικός / sēmantikos, which means “significant.” This Greek term is derived from σημαίνω / sēmaino, meaning “to show or indicate by a sign,” which in turn comes from σημα / sēma, meaning “sign, mark, token; portent; constellation.” In the field of semantics, communication patterns incorporate signs that help to convey specific meanings.e
In this article, readers will find a concise yet comprehensive definition of semantics. By the end of the text, readers will grasp the essence of semantics and recognize its importance. Moreover, this article introduces new perspectives and concepts within the realm of semantics, including confirmational and corrective loops.
- What is The Meaning of Semantics in Linguistics?
- Why Semantics?
- Why is Semantics crucial for Communication?
- Understanding Context: Why is Semantics necessary for understanding?
- Why is Semantics important for Language Development and Language Evolution?
- Why do Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning need semantics?
- Why is semantics used in online marketing and search engine optimization?
- What are examples of the successful transformation of information?
- What is the core idea of semantics?
- What do intention and interpretation mean in the context of semantics?
- Is successful semantic communication a matter of willingness?
- What can people do to make communication happen better?
- What concepts of semantics exist?
Why Semantics?
There are several Why’s in Semantics. Semantics is a fundamental concept of successful sending and understanding meaning between at least two entities, such as humans and machines. Language is more than stringing words or signs together. Semantics is about conveying ideas and information effectively. Here are the main communication fields where the concept of semantics is used: Communication, Understanding Context, Language Development and Language Evolution, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, online marketing and search engine optimization.
Why is Semantics crucial for Communication?
Semantics helps to understand what others are saying, and it helps convey the own thoughts and feelings. This could range from simple requests like “Pass me the salt” to more complex phrases, ideas and arguments.

Understanding Context: Why is Semantics necessary for understanding?
Semantics helps man and machines to determine the meaning of a noun in different contexts. The concept of semantics helps to detect the differences of meaning, determined by a given context. For example, the word “bat” can refer to an animal, a piece of sports equipment, or the act of batting in a game, depending on the context.
Why is Semantics important for Language Development and Language Evolution?
Semantics is important for Language Development and Language Evolution, because language evolves within and between the societies and cultures it is used. Semantics helps man to track these changes and understand how meanings of words and phrases can shift over time.
Why do Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning need semantics?
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning need semantics for Natural Language Processing, Natural Language Understanding, and Natural Language Generation. In sum: Semantics is a link between computational language and human language. The key techniques are search engines, voice assistants, and automatic translation services.
Why is semantics used in online marketing and search engine optimization?
The semantic search is on the rise. The semantic web is growing. That’s why online marketing and search engine optimization are using semantics.
What are examples of the successful transformation of information?
2 Examples of a well-functioning transfer of information between humans:
Example 1: A wife tells her husband on the phone to buy something for dinner – and the husband buys exactly what the woman wanted. This understanding is by no means a matter of course. It could have gone wrong.
Example 2: A teacher explains the principle and the worth of peace – and the class is stopping any bullying.
What is the core idea of semantics?
This is the basic idea of semantics in one sentence by Johannes Faupel. “For successful communication, two positions have to match: Intention and Interpretation.”
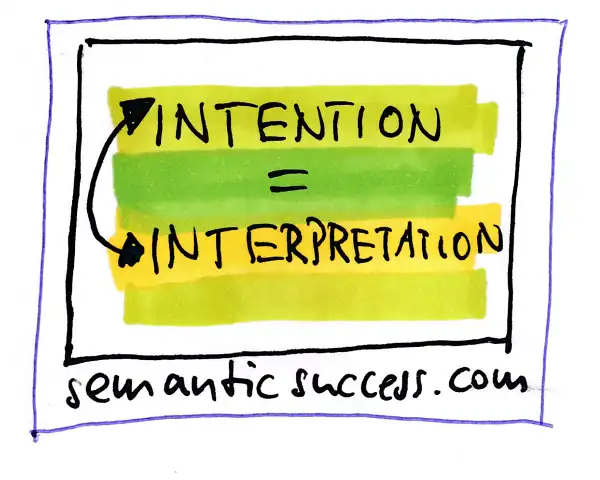
What do intention and interpretation mean in the context of semantics?
Intention in the context of semantics means The wish or plan of a sender to develop a full understanding of his intended meaning to a recipient.
Interpretation in the context of semantics is a result of 2 main factors.
Factor 1: A person’s willingness or refusal of developing an understanding.
Factor 2: A person’s capability or lack of developing an understanding Factor.
Semantics is all about matching a signal’s core substance on the way from a sender to a recipient or a group of recipients.
Is successful semantic communication a matter of willingness?
No, communication is not depending on the pure will of talking or writing to others. Often, there are too many disturbing signals between the sender and the recipient.
The disturbing signal of speed: There may be the lack of time. Half of the message or even more cannot be heard.
The brain brake of “knowledge”: Too fast conclusions on the recipient’s side hinder the recipient from discovering the meaning: “I know what he means”.
The linguistic gap: Linguistic issues like different native languages may interrupt communication.
What can people do to make communication happen better?
First, we have to understand and accept that talking is no communication, and writing is no communication. If we accept this, we will be able to build in our communication processes confirmation loops and correction loops.
What are confirmation loops in communication?
Confirmation loops is a new concept in semantics by Johannes Faupel, the author of this website. It describes the process of recurring questions on both sides of a communication pair: Did you understand anything? What did you understand? Do you know what I want to express? Confirmation loops in communication are based on a process of continuous communication research: “How did you understand what I said or wrote?” Confirmation loops can be used in meditation processes based on non-violent communication (Marshall B. Rosenberg), they can be used in education and on the web.

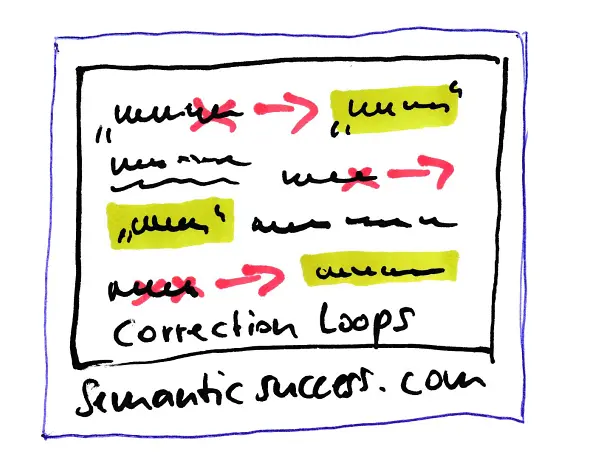
What are correction loops in communication?
Correction loops are based on the willingness of both the sender and the recipient to change their view on the result of a communication process so far.
What concepts of semantics exist?
Concepts of semantics – learn more about Linguistics, Formal semantics, Conceptual semantics, Cognitive semantics, Lexical semantics, Cross-cultural semantics, Computational semantics.
There will be soon deeper information about confirmation loops and correction loops in the communication process. Subscribe to the free newsletter with semantic success information.